The Complete Guide to Studying Engineering in Malaysia
How many As do you need to study engineering? Learn more on entry requirements, scholarships and fees in this comprehensive guide.
Have you always been fascinated with how things work in the world? Do you love to solve complex puzzles and create something new? Are you excellent in maths and science, too? If so, chances are you’ll want to become a successful engineer!
This comprehensive guide will take you through everything you need to know about engineering courses in Malaysia, from the different types of engineering courses and the best engineering universities all the way to your career options as a holder of an engineering graduate degree.
Want to find the best engineering course for you and build a better world? Keep reading!
Asia Pacific University of Technology & Innovation (APU)
APU Foundation Programme (Engineering)
✓Programme emphasises on 4 key areas – leadership and teamwork, problem-solving skills, social skills and responsibilities, and practical skills – that will lead to excellence in your education performance, as well as career-readiness
#1. What is Engineering?
Engineering is the application of maths and science to design and build things to help improve people’s lives.
By applying scientific, economic and mathematical knowledge, engineers work to design, build, maintain and improve all sorts of things, including structures, machines, electronic devices, systems and processes.
You may wonder, what is the difference between scientists and engineers?
As Albert Einstein once said, “Scientists investigate that which already is; engineers create that which has never been.” For instance, a scientist may discover and explain the concept of electromagnetic radiation but it takes an engineer to build a television.
Nearly every single aspect of your everyday life involves engineering. From buildings, roads and roller coasters to your smartphones, laptops and LEGO blocks, many of these inventions would not exist without the skillful work of an engineer.
With a Degree in Engineering, you’ll learn to apply maths, science and engineering principles, solve various engineering problems systematically and design solutions and systems to help solve health and safety, cultural, societal and environmental concerns. You’ll also be able to develop engineering products, processes and systems that are safe, effective, economical and sustainable.
Types of Engineering Courses
As engineering is an extremely broad discipline, there are many specialised fields of engineering. Here are four of the major branches of engineering.
| Field | What It Is All About |
|---|---|
| Civil Engineering | Deals with designing, constructing, operating and maintaining physical and built environments, such as roads, railways, buildings, dams and wastewater service facilities. |
| Chemical Engineering | Deals with the efficient process of converting chemicals and raw materials into more useful and valuable materials. Examples include petroleum refining, food processing and plastic production. |
| Electrical & Electronic Engineering | Deals with designing, developing and operating electrical systems and machinery (electrical) and electronic circuits and devices (electronic). Examples include harnessing energy from alternative resources and designing microprocessor-based computer systems. |
| Mechanical Engineering | Deals with the design, construction and operation of machines and mechanical systems, such as vehicles, industrial equipment and medical devices. |
Other fields of engineering include: Aeronautical Engineering (air and space vehicles), Petroleum Engineering (drilling and producing crude oil and natural gas), Environmental Engineering (improvement of the environment) and Mechatronics (mechanical and electrical engineering to design automated systems).
In many universities, you will be required to decide which discipline of engineering you would like to study for your undergraduate degree. For example, if you choose the Mechanical Engineering discipline, you will be pursuing a Bachelor of Engineering (BEng) in Mechanical Engineering.

#2. Engineering Course Requirements
a) Subjects required for engineering
To study engineering, the required subjects at SPM or equivalent are:
- Mathematics
- Science
- English
Thereafter, the required subjects for engineering at A Levels, STPM or equivalent are:
- Mathematics
- Physics
- Further Mathematics (recommended A Levels subject) or Specialist Mathematics (recommended Australian Matriculation subject)
b) Requirements for Engineering Diploma
These are the general entry requirements for a Diploma in Engineering:
- SPM (or equivalent): Minimum 3Cs, including Mathematics and Physics/Chemistry or General Science as well as a pass in English
c) Requirements for Engineering Degree
To pursue a Degree in Engineering, you need to complete a pre-university programme and meet the entry requirements.
- A Levels: Minimum 2Ds including Mathematics and Physics/Chemistry
- STPM: Minimum 2Cs including Mathematics and Physics/Chemistry
- Foundation in Science or Foundation in Engineering: Minimum CGPA of 2.00
- Diploma: Minimum CGPA of 2.00
In addition, it is advisable to have at least a C in Mathematics and Physics/Chemistry as well as a pass in English at SPM level.
#3. Studying Engineering in Malaysia
a) What do you study in engineering?
Here are some of the engineering subjects you’ll study in each field:
| Field | Subjects |
|---|---|
| Civil Engineering | Civil Engineering Materials, Structural Mechanics, Surveying, Geotechnics, Environmental Engineering, Hydraulics, Coastal / Highway / Traffic Engineering |
| Chemical Engineering | Thermodynamics, Process Engineering, Fluid Mechanics, Industrial Chemistry, Reaction Engineering, Plant Design |
| Electrical & Electronic Engineering | Digital & Analogue Electronics, Signal Processing, Control Systems, Circuit Design, Computer Architecture, Power Electronics |
| Mechanical Engineering | Thermodynamics, Fluid Mechanics, Solid Mechanics, Automatic Control & Instrumentation, Machine System Dynamics |
You will also have individual and group projects that require you to design, build and test a new product or a technical solution. This allows you to gain valuable experience in building things and solving problems, which are necessary once you graduate and start work as an engineer.
Additionally, you will also be required to complete at least 2 months of industrial training (i.e. internship) to gain exposure to the industry.
b) How long is an engineering degree?
An Engineering Degree is usually 4 years long, but some universities may offer 3-year degrees.
If you intend to gain status as a professional engineer, we recommend that you pursue a 4-year degree in engineering based on the guidelines by the Board of Engineers Malaysia (BEM).
c) How much does it cost to study engineering in Malaysia?
The estimated cost to pursue a Degree in Engineering is between RM35,000 – RM315,000.

Asia Pacific University of Technology & Innovation (APU)
Bachelor of Computer Engineering (Hons)
✓Fully accredited by the Board of Engineers Malaysia (BEM) which is a signatory to the Washington Accord
#4. How to Be an Engineer in Malaysia
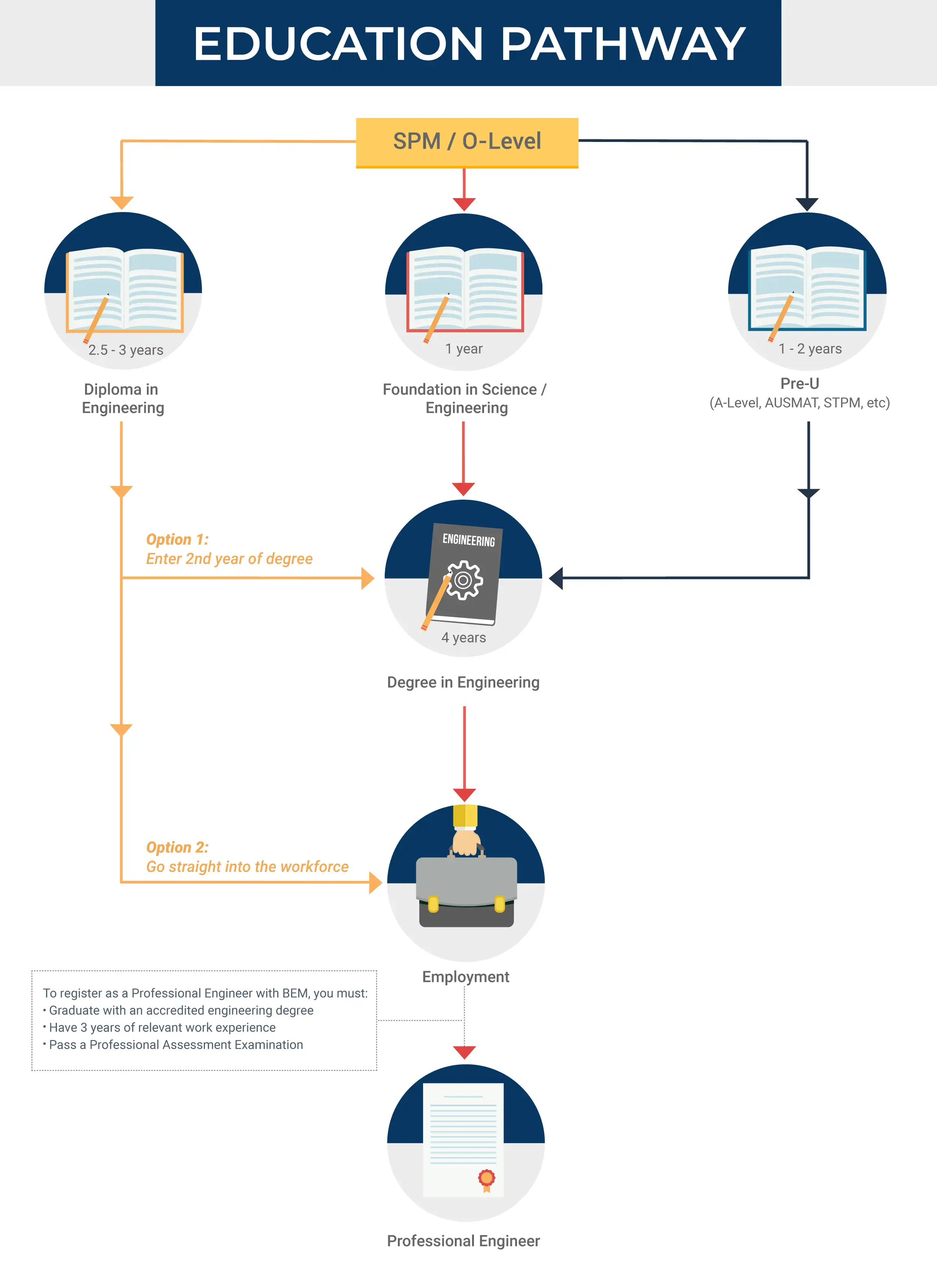
How many years does it take to become an engineer? Do you need a professional qualification in engineering? Read on to find out more about the engineering pathway.
Step 1: Complete a pre-university, foundation or diploma
First, you’ll need to complete a pre-university (e.g. A Levels, STPM) or a Foundation course (e.g. Foundation in Engineering, Foundation in Science) after SPM. This will typically take 1 – 2 years depending on the selected programme.
Alternatively, you can also pursue a Diploma in Engineering which usually takes between 2.5 and 3 years. A diploma qualification will give you the option of either entering the workforce in relevant fields upon graduating or continuing with a Degree in Engineering, starting in Year 2.
Step 2: Complete an accredited 4-year Degree in Engineering
Subsequently, you can enrol in a Bachelor of Engineering in Malaysia, which usually requires 3 – 4 years of study.
If you wish to gain professional status as a professional engineer in Malaysia, you must study an accredited Engineering Degree with a duration of 4 years. Otherwise, you will need to complete a further learning programme called the BEM-Graduate Assessment Program (BEM-GAP), which will add another 2 years to your educational journey.
Step 3: Register as a Graduate Engineer
After completing your engineering degree, you will be eligible to register with BEM as a Graduate Engineer. After completing 3 years of practical work experience, you can sit for the Professional Assessment Examination (PAE) by BEM.
Step 4: Register as a Professional Engineer
Once you have gained sufficient practical work experience and passed the PAE, you will be able to register as a Professional Engineer.
As a professional engineer, you can use the abbreviation “Ir.” before your name or “P.Eng.” after your name to denote your professional engineer status.
In summary, it takes at least 5 – 6 years from SPM to become an engineer and 8 – 9 years to become a registered professional engineer.

#5. Should You Study Engineering?

a) Is engineering the right course for you?
If you’re wondering whether you should study engineering, here are some questions to think about:
- Are you skilled at practical work?
- Do you consider yourself mechanically inclined?
- Do you enjoy building LEGO structures?
- Do you like to tinker with machines and electronic devices?
- Can you think logically and solve complex math problems?
- Are you able to work independently with little supervision?
- Do you have good grades in maths and physics?
If you answered yes to most of these questions, engineering may be the right choice for you!
b) Skills required to be an engineer
Here are some key skills a good engineer should have:
- Critical thinking skills to solve complex problems
- Active listening skills
- Strong IT and technical skills
- High level of scientific knowledge
- Creative and innovative thinking
- Keen attention to detail
- Organisational and management skills

Asia Pacific University of Technology & Innovation (APU)
APU Foundation Programme (Engineering)
✓Programme emphasises on 4 key areas – leadership and teamwork, problem-solving skills, social skills and responsibilities, and practical skills – that will lead to excellence in your education performance, as well as career-readiness
#6. What Can You Do With an Engineering Degree in Malaysia?
A Degree in Engineering will prepare you for a career in various sectors, including oil & gas, manufacturing, construction, logistics and automotive.
Below are some of the engineering jobs in Malaysia that you can pursue upon graduating:
| Field | Career Options |
|---|---|
| Civil Engineering |
|
| Chemical Engineering |
|
| Electrical & Electronic Engineering |
|
| Mechanical Engineering |
|
#7. Best Engineering Universities in Malaysia
If engineering is right up your alley, then check out some of the best universities for engineering in Malaysia. Alternatively, you may want to compare more universities for Engineering Degrees or Engineering Diplomas.
Asia Pacific University of Technology & Innovation (APU)
Bukit Jalil, Kuala Lumpur
Bachelor of Electrical & Electronic Engineering (Hons)
Intake
Mar, Jul, Sep
Tuition Fees
RM118,400
Get RM500 Waiver + RM300 Rebate when you enrol through EduAdvisor! T&C apply.