Biomedical Science vs Biomedical Engineering: What's the Difference?
Biomedical science and biomedical engineering — are they the same thing? They are in fact two distinct fields of study. Explore the major differences in this article.
Updated 05 Jan 2023
Both biomedical science and biomedical engineering contribute to treating diseases and aiding in the medical and healthcare field, but are they the same thing? And does it matter whether you study one or the other?
Despite being part of the biomedical field, both biomedical science and biomedical engineering have contrasting features that can lead to different career pathways.
Here’s what you need to know about the differences between biomedical science and biomedical engineering so you don’t make the wrong choice.
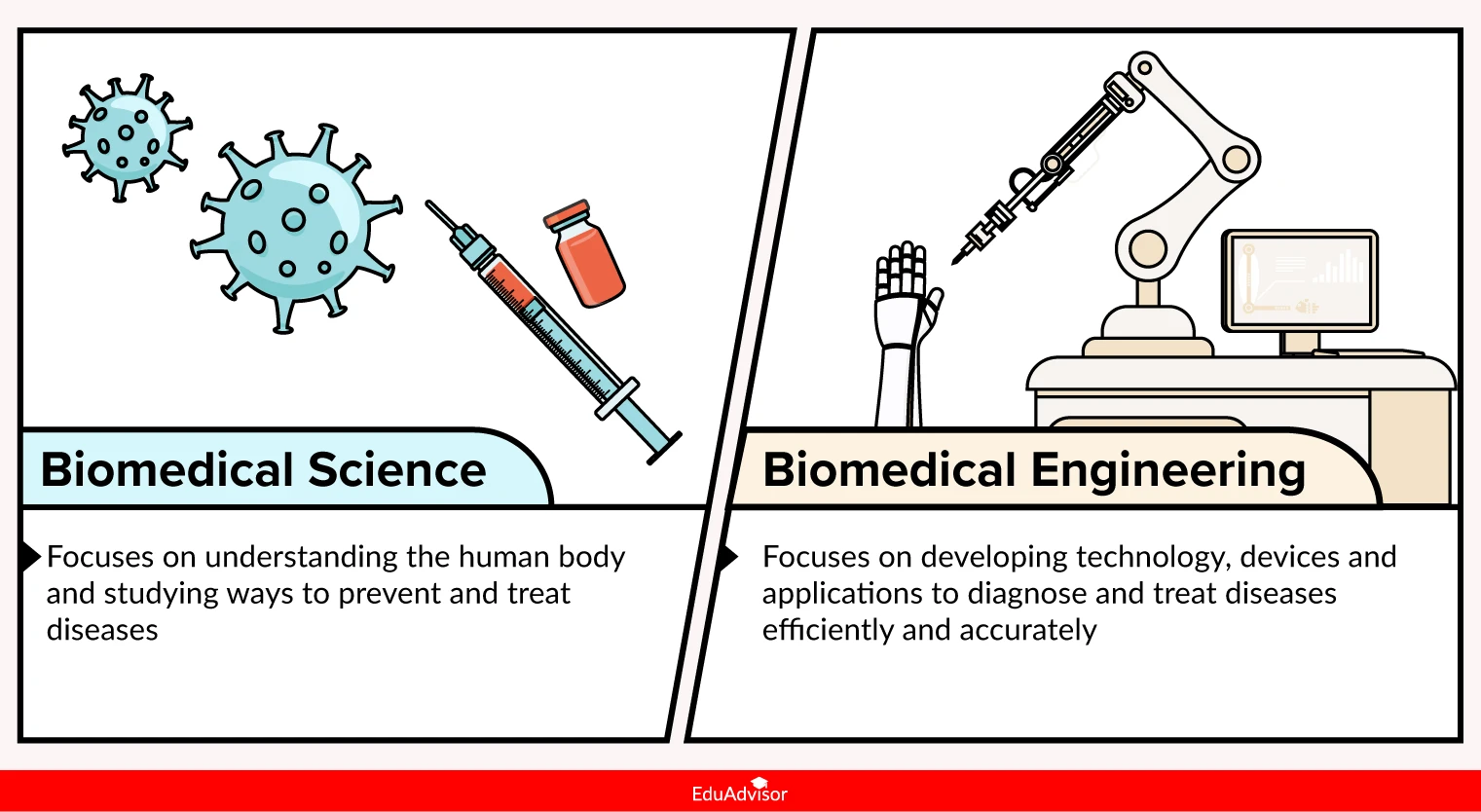
#1. Biomedical science focuses on the research for treating diseases while biomedical engineering is about creating technology and devices
Both biomedical science and biomedical engineering are about making advancements in healthcare and improving human health but the difference lies in how they are executed.
Biomedical science is about understanding the human body and studying ways to prevent and treat diseases. Biomedical scientists conduct research to investigate various medical conditions — think cancer, blood disorders and hepatitis — to identify the causes and ways to treat them. This research can lead to the development of new treatments and drugs.
Biomedical engineering, on the other hand, focuses on applying engineering principles to improve the healthcare field. A cross-discipline that spans the fields of biology, medicine and engineering, biomedical engineers develop technology, devices and applications to diagnose and treat diseases efficiently and accurately. Some popular biomedical engineering products include prosthetic limbs, 3D organ printers and medical imaging technology (e.g. MRI, CT scan, ultrasound).
In short, biomedical science is about understanding the fundamental principles of the human body and its functions while biomedical engineering uses this knowledge to design and develop medical solutions and technologies.
Asia Pacific University of Technology & Innovation (APU)
Bachelor of Petroleum Engineering (Hons)
✓Accredited by the Board of Engineers Malaysia (BEM) and Washington Accord
#2. Biomedical science is a health science field while biomedical engineering is a subset of engineering
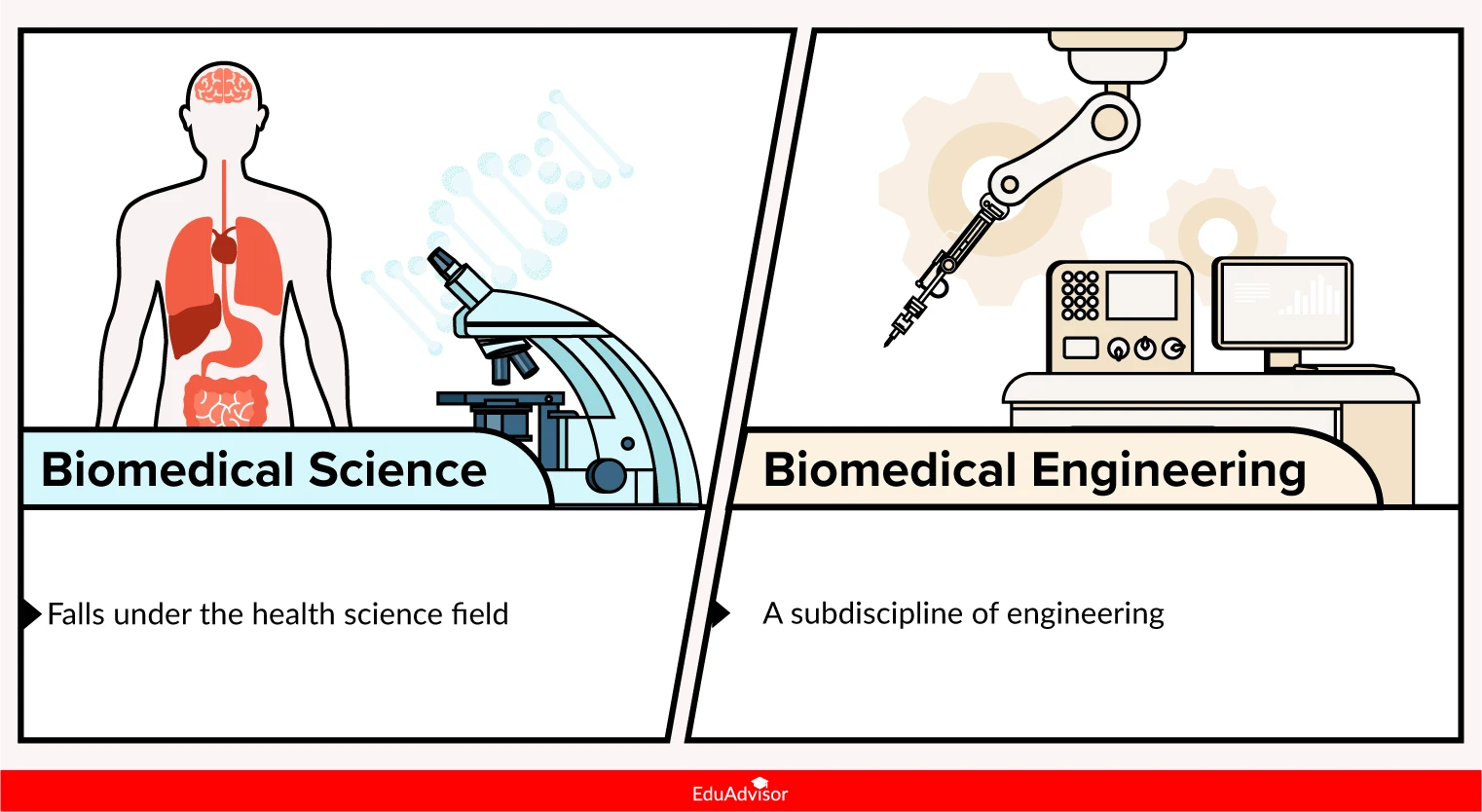
Despite sounding similar, they both actually belong to two different fields of study.
Biomedical science falls under the medical and health science field and covers aspects of laboratory diagnosis, disease prevention and research. It includes a wide range of subfields such as molecular biology, genetics, microbiology, immunology and pharmacology. From the molecular level up to the level of organ systems, each of these subfields allow biomedical scientists to gain a more detailed and comprehensive understanding of the body and how it works.
Biomedical engineering, on the other hand, is a subdiscipline of engineering. The field integrates almost all aspects of engineering (mechanical, electrical, chemical) with human biology to develop practical solutions to real-world problems in healthcare. Biomedical engineers can specialise in areas such as bioinstrumentation, biomaterials, tissue engineering and biomechanics.
As a field of study, universities often offer biomedical engineering under the faculty of engineering while biomedical science is typically placed under the health and medical science faculty.

#3. Both programmes cover different subject materials
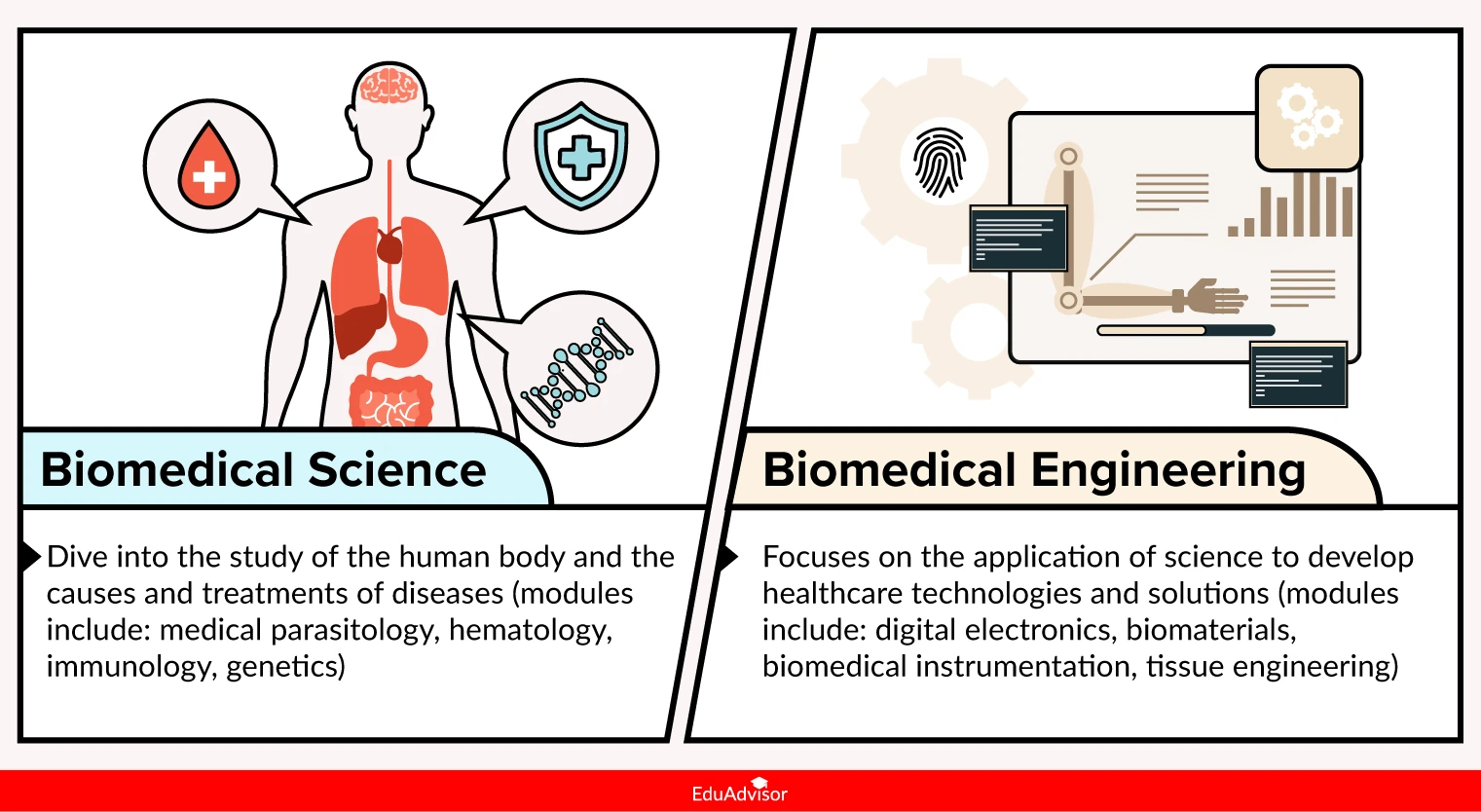
Although biomedical science and biomedical engineering are closely related, they are ultimately two distinct fields of study. Therefore, the subjects that you learn will be different too.
With a biomedical science degree, you will cover basic and advanced science modules including medical parasitology, hematology, immunology, genetics, microbiology and pharmacology. Additionally, you will also spend time doing diagnostic lab work (e.g. biochemistry tests, preparing tissue samples for microscopic examination, operating a microtome to slice tissues) as well as research work.
Meanwhile, a biomedical engineering degree will see you focusing on applying engineering and computer science principles to medicine and healthcare. This will be done through topics such as digital electronics, biomaterials, biomedical instrumentation and tissue engineering. Practical work may include designing and soldering electrical circuits, programming and signal processing.
That being said, there may be overlapping modules such as anatomy and physiology.
In short, biomedical science will dive into the study of the human body and the causes and treatments of diseases while biomedical engineering will look at the application of science to develop healthcare technologies and solutions.
Apply for university with EduAdvisor
Secure scholarships and more when you apply to any of our 100+ partner universities.
Start now#4. Biomedical science has a higher entry requirement than biomedical engineering
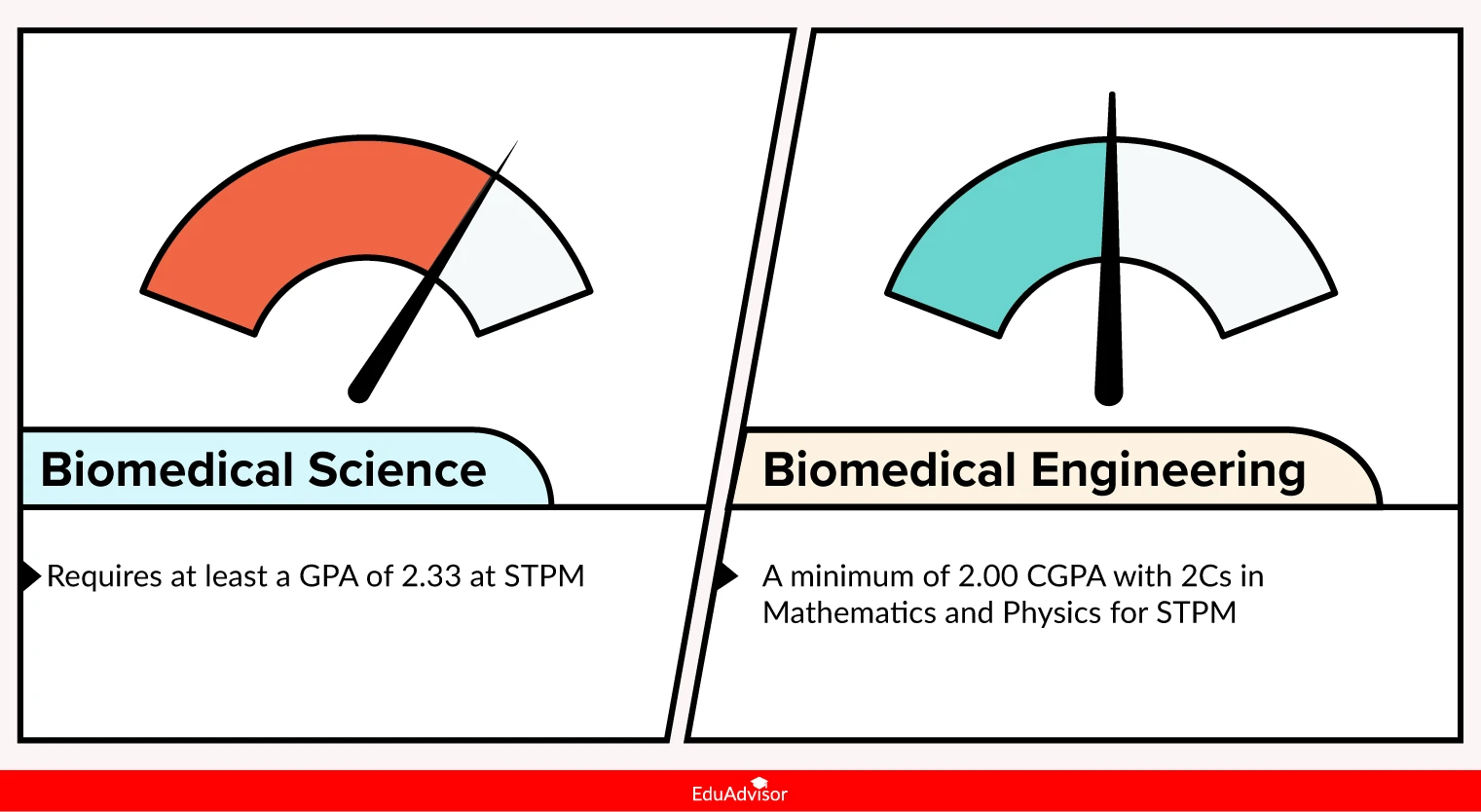
In Malaysia, biomedical science commands a higher entry requirement than biomedical engineering as dictated by the Malaysian Qualifications Agency (MQA).
To study biomedical science, you’ll need to have at least a GPA of 2.33 at STPM (or equivalent) in two of the following subjects — Biology, Physics / Mathematics, or Chemistry.
In contrast, biomedical engineering only requires you to have a CGPA of 2.00 with a minimum of 2Cs in Mathematics and Physics at STPM or equivalent.
However, whether it’s biomedical science or biomedical engineering, universities may require you to have better grades, so it’s good practice to check with the universities beforehand.

Asia Pacific University of Technology & Innovation (APU)
Bachelor of Petroleum Engineering (Hons)
✓Accredited by the Board of Engineers Malaysia (BEM) and Washington Accord
#5. A biomedical science degree has a shorter duration than a biomedical engineering degree
As biomedical science is a science degree, universities often offer biomedical science as a 3-year programme. As part of your studies, you will attend lectures and work on coursework related to biology, chemistry and medicine, gain laboratory experience and work on a research project.
On the other hand, since biomedical engineering is an engineering degree, it is often structured as a 4-year degree programme. A biomedical engineering degree will typically include lectures and coursework related to engineering, biology and medicine, laboratory experience and design projects.

#6. Both fields boast different career prospects
As a biomedical science graduate, you will be able to pursue a variety of careers in the pharmaceutical, biotechnology and healthcare fields working in research, lab diagnostics or quality assurance. Jobs in the field include biomedical scientist, research scientist, microbiologist, laboratory technologist and bio-entrepreneur. You may also choose to continue your education and pursue a postgraduate research degree.
If you’re keen on the engineering aspects of the medical field, biomedical engineering is where it’s at. A biomedical engineering degree will enable you to work in roles such as medical device engineer, biomaterials engineer, rehabilitation engineer and biomedical engineer where you will design and develop medical devices and solutions. There is also opportunity for you to work in emerging areas such as bioinformatics, telemedicine and biomedical computing.
There you have it! We hope this guide gives you a clearer understanding between these two fields. In short, biomedical science concerns the study and understanding of the human body and health while biomedical engineering provides the solutions related to human health.