MBBS vs MD: What’s the Difference?
What is the difference between an MBBS and MD? Does it matter which one you choose? Learn all you need to know about the two qualifications here.
Published 15 Sep 2022

If you’re planning to become a doctor, you’ll have to pursue a medical degree. And if you’ve been checking out numerous medical schools, you probably would have noticed that there are different degree awards for medicine — namely, Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS) and Doctor of Medicine (MD).
But how does an MD differ from an MBBS? Is an MD a higher qualification compared to MBBS? What about the study duration and programme structure?
The answer to these questions depends highly on the university, the awarding body and the country. In this article, we explain the similarities and differences between an MBBS and an MD based on the medical degrees that are offered in Malaysia, as well as in Australia and the UK.
#1. What’s the level of study for an MBBS and MD?
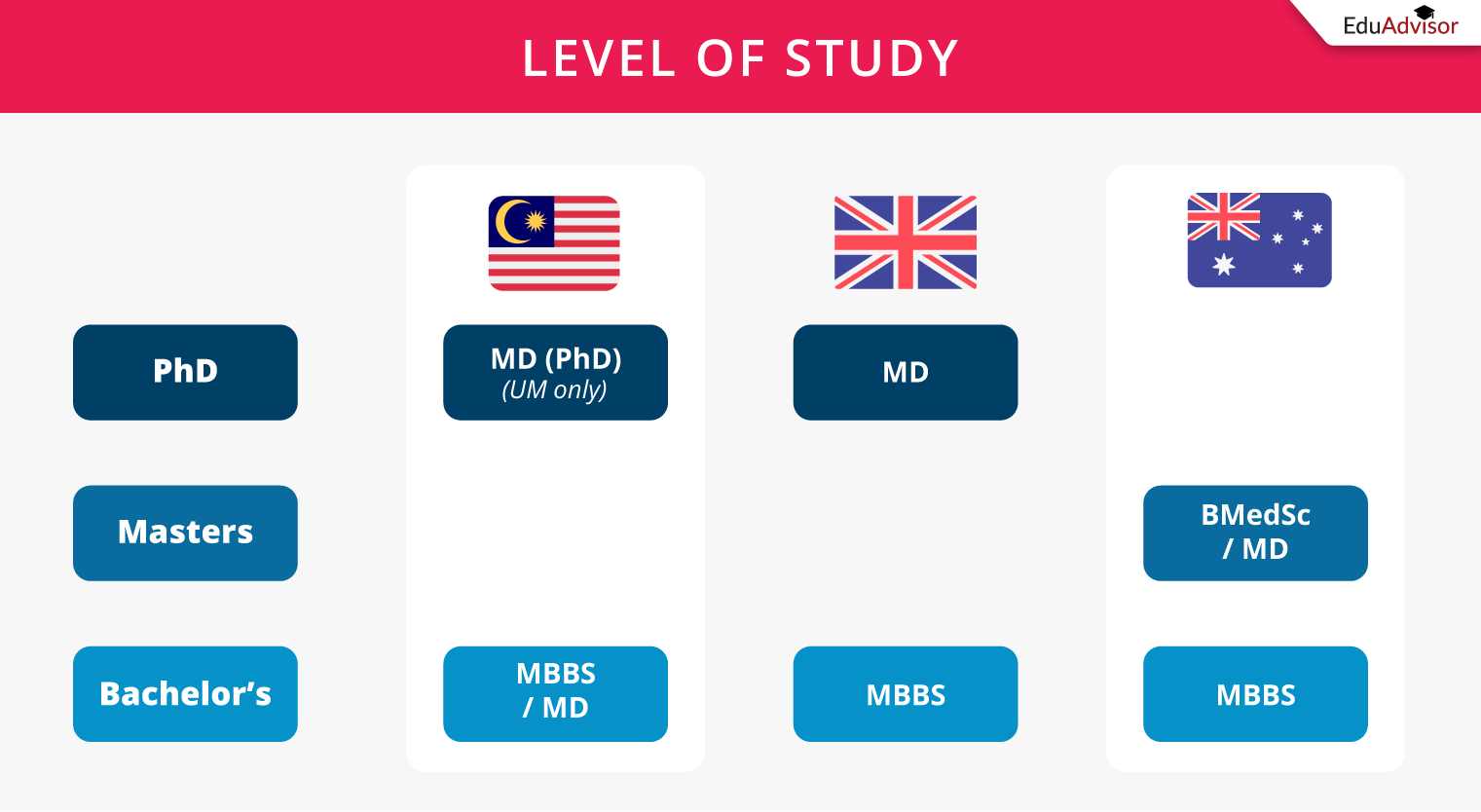
With the term ‘Doctor’ in Doctor of Medicine, you may think that an MD is at the doctorate level and is a higher level of qualification compared to a Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS). However, that may not always be the case.
Malaysia
In Malaysia, both the MBBS and MD are bachelor’s degrees and are of the same level of qualification. To pursue this programme, you will need a pre-university or foundation qualification (e.g. A Level, STPM, Foundation in Science).
The only exception to this is Universiti Malaya (UM) which offers MD at a doctorate level, the only Malaysian university to do so. As a PhD qualification by research, you’ll need an MBBS and a master’s degree or specialist qualification to qualify for the programme.
UK
In the UK, an MBBS is a bachelor’s degree while an MD is a postgraduate qualification, specifically a doctoral research degree. This means that you can only pursue the MD after completing your first degree, which is typically an MBBS.
Australia
Historically in Australia, medical schools used to award the MBBS as a bachelor’s degree and the MD as a doctoral research degree.
However, most Australian medical schools have transitioned to awarding the MD — either as a graduate entry programme (indicated as Doctor of Medicine (MD), which means you’ll need a bachelor’s degree to pursue the programme) or a combination of a science degree together with an MD (for instance, Bachelor of Medical Science/Doctor of Medicine (BMedSc/MD) or Bachelor of Clinical Science (Medicine) / Doctor of Medicine (BClinSci/MD), where you can apply for the programme with a pre-university qualification).
Regardless of whether the MD is a graduate entry programme or a non-graduate entry programme, the MD is recognised as a ‘Masters Degree (Extended)’ in Australia, which is a higher level compared to a bachelor’s degree.
DID YOU KNOW
Graduate entry medical programmes require you to first take a bachelor’s degree programme. This often allows you to pursue medical education in a shorter time frame compared to the standard non-graduate entry.

#2. How long are an MBBS and MD?
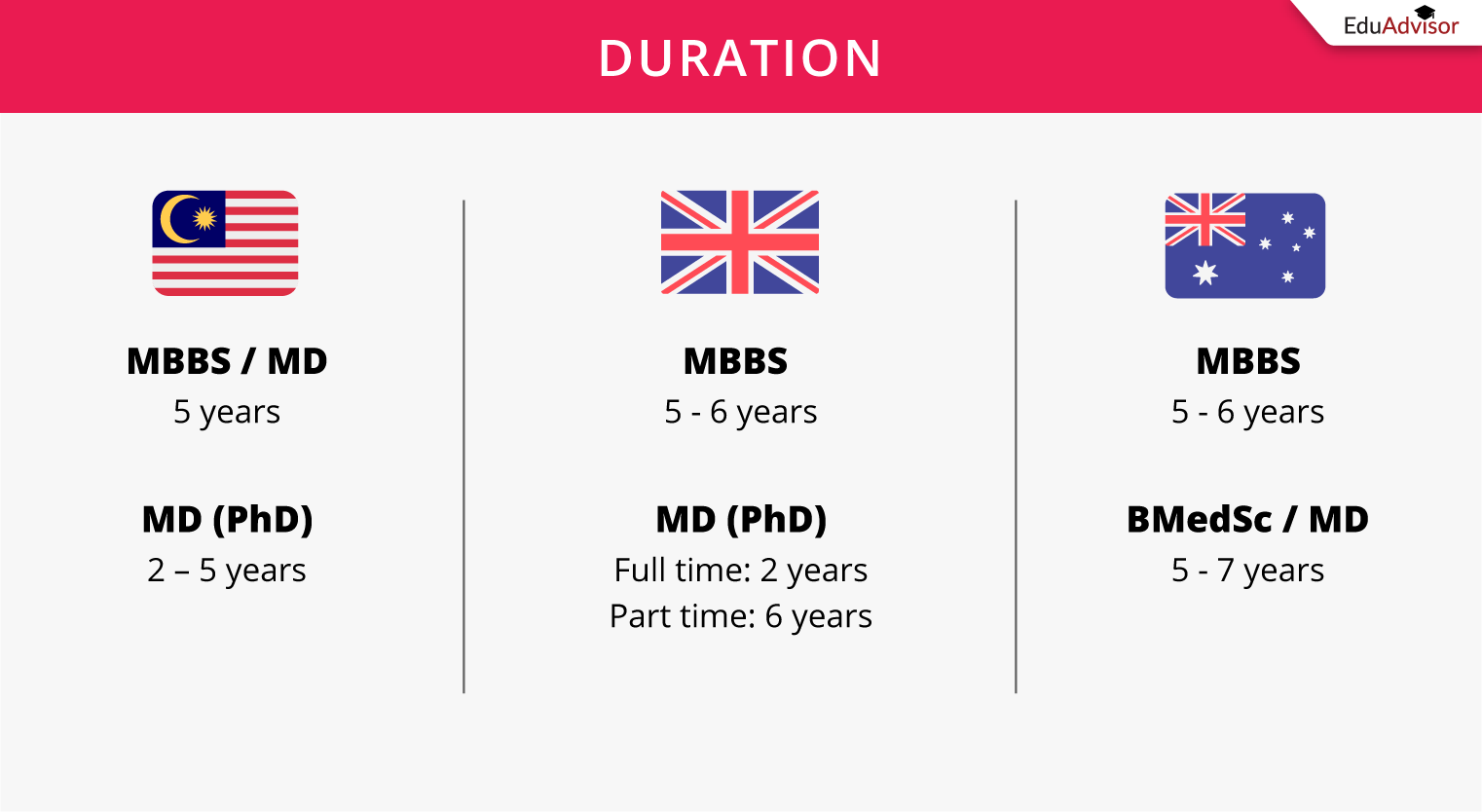
Typically, most undergraduate medical degrees take 5 years to complete. However, the duration can be longer depending on the country and awarding institution.
Malaysia
In Malaysia, the standard course length for an undergraduate medical degree (regardless of whether it’s an MBBS or an MD) is 5 years. The exception to this is at universities that offer medicine as a graduate entry medical programme, where the programme duration is 4 years.
The MD at Universiti Malaya (which is a postgraduate doctoral research degree) is approximately 2 – 5 years long.
UK
The MBBS in the UK, however, can take between 5 – 6 years to complete. While the standard duration is 5 years, some medical schools offer students the option of intercalating. This allows students to take a year out of medical school to study a specific area of interest, gain new knowledge and develop new skills. If you choose to take an intercalated year, you’ll be able to study and gain an additional degree alongside your MBBS.
As for the MD in the UK, it typically takes 2 years for full-time and 6 years for part-time.
Australia
The MBBS degrees in Australia usually take between 5 – 6 years to complete. However, few universities in Australia offer the MBBS as many have moved to offer a combined medical science degree with the Doctor of Medicine.
If you’re taking a combined medical science degree with MD (e.g. BMedSci/MD), the duration of your studies will be approximately 5 - 7 years depending on the university. As a graduate entry programme, the MD in Australia is 4 years. This means that you’ll be required to study a science-related bachelor’s degree before taking an MD.
Apply for university with EduAdvisor
Secure scholarships and more when you apply to any of our 100+ partner universities.
Start now#3. What is the programme structure for MBBS and MD?
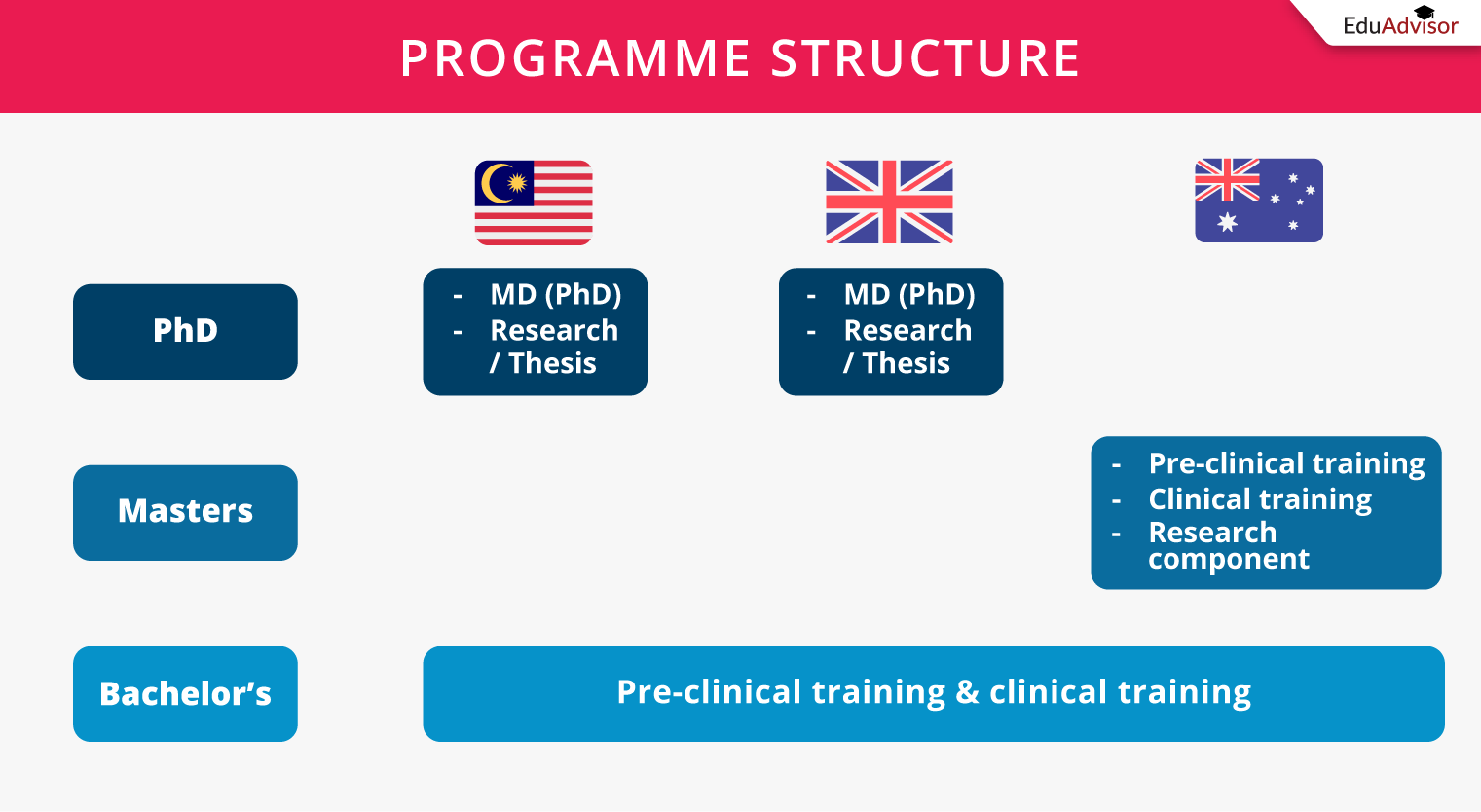
Generally, any medical degree will include 2 phases — pre-clinical training and clinical training. This applies to all 3 countries. During the first 2 years of your degree, you’ll focus on your pre-clinical training where you’ll cover the theoretical aspects of basic medical science. Thereafter, you’ll continue with your clinical training where you will experience hands-on training at hospitals and health clinics.
As an extended masters degree in Australia, the combined science/MD degree will have an extra research component that is to be completed during the clinical years.
For all postgraduate doctoral research MDs, you will need to conduct and publish a research paper or thesis before you are awarded a PhD.
#4. Can you become a doctor if you have an MBBS or MD?

If you’re wondering whether you can become a doctor with either an MBBS or MD, the answer is yes.
In Malaysia, both the MBBS and MD (undergraduate) degrees are recognised by the Malaysian Medical Council (MMC) and can propel you to become a doctor. You’ll need to complete your housemanship and necessary training before completing the full registration as a medical officer and use the abbreviation “Dr.” in front of your name.
In the UK, medical students graduating with an MBBS will need to register with the General Medical Council in order to practise medicine.
As for Australia, both MBBS and combined science/MD degrees awarded at any Australian medical school will qualify you to register with the Medical Board of Australia and ultimately work as a doctor.
Which should you choose, an MBBS or MD?

If you’re pursuing your medical education in Malaysia, both the MBBS and MD (undergraduate) are appropriate degrees for you to pursue. Both comply with the standards set by MMC and the Malaysian Qualifications Agency (MQA) and will provide you with the right skills and knowledge to become a qualified doctor.
Instead, consider comparing the costs, programme structure, specialised facilities, clinical exposure (location of hospitals as some can be out of state), overseas transfer options and degree recognition. These factors can greatly affect your learning.
On the other hand, if you’re pursuing your medical degree in Australia (or an Australian university with a branch campus in Malaysia), you’ll need to consider the fact that there will be an additional research component as part of your studies if you choose a combined science/MD degree. Do note that the level of masters degree (extended) for MD is recognised only in Australia and not in Malaysia by MQA.
So there you have it. We hope this guide has helped you understand the difference between MBBS and MD. Bear in mind that neither programme is better than the other — it boils down to various factors, so take some time to digest these considerations before jumping into a decision.






