Biotechnology vs Biomedical Science: What’s the Difference?
What’s the difference between biotechnology and biomedical science? Aren’t they the same thing? Well, not really.
Updated 14 Aug 2021
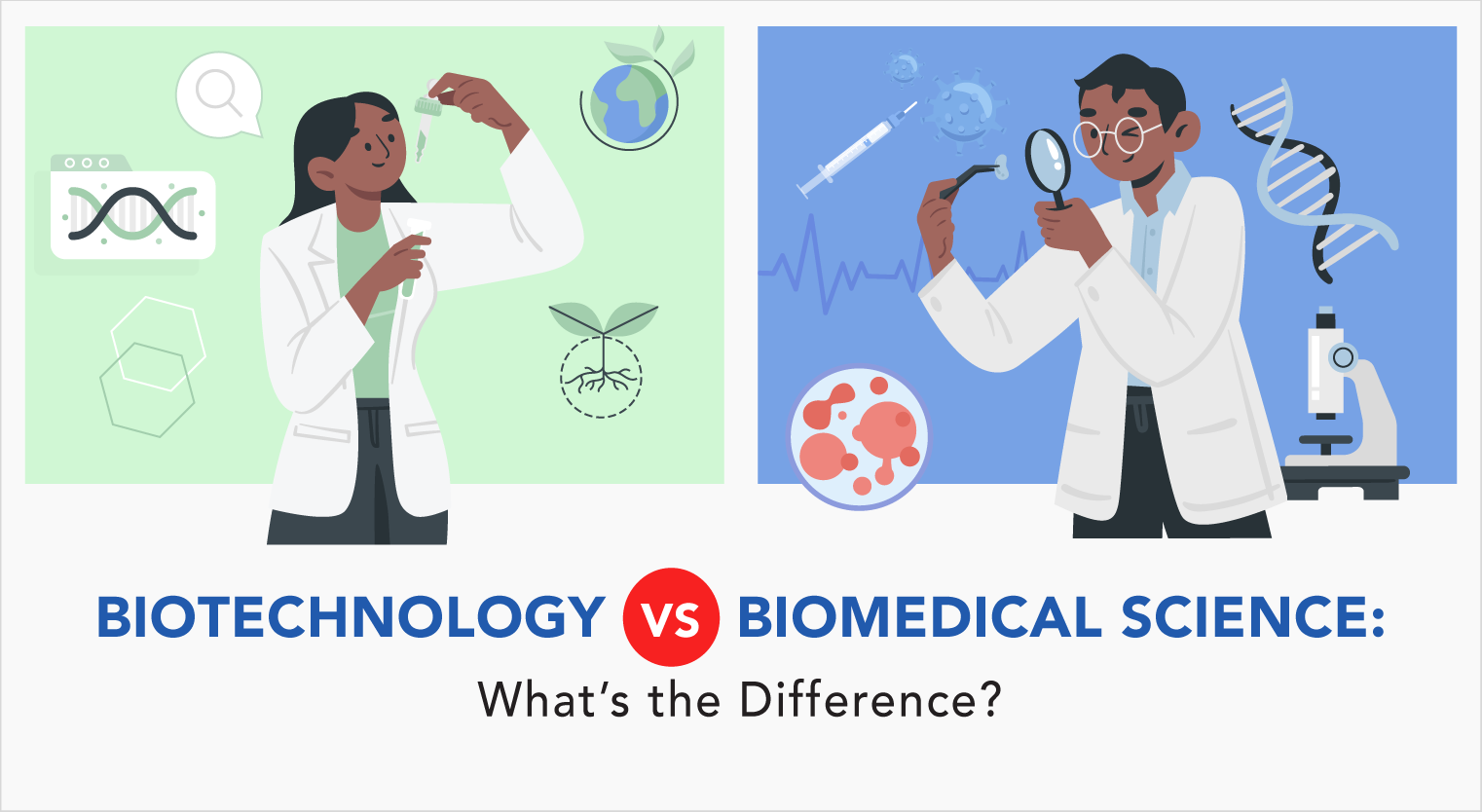
Biotechnology or biomedical science? Wait — aren’t they the same thing?
It’s easy to misunderstand what these fields truly entail and use the terms interchangeably. After all, they’re both part of the bioscience field. So they should be about biology and science, right?
Well, there’s more to them than that. Here are 4 key differences between biotechnology and biomedical science.
#1. Biomedical science centres on the “what” while biotechnology focuses on the “how can we fix it”
While both biomedical science and biotechnology involve the study of life (hence the prefix bio), the two fields focus on different things.
Biomedical science is the study of the human body to prevent and treat diseases. The field looks at the “what”, “how” and “why” of the human body. Biomedical scientists conduct research to study a variety of conditions ranging from cancer and diabetes to stress and ageing. The research goes a long way in the development of new drugs, treatments and therapies.
Biotechnology, on the other hand, is the genetic manipulation of living organisms to develop new technology and products. It is more interested in answering the question of “what can we do to fix something”. Examples of products created by biotechnology are biodegradable plastics, GMOs like corn and seedless watermelon, and biodetergent.
#2. You will study different subjects although there may be some overlapping modules
If you choose to pursue biotechnology, you will cover a variety of subjects around the topic of bioscientific principles and knowledge and bioinformation technologies. Some of the modules you will cover include bioprocessing technologies, genetic engineering and molecular cloning.
In contrast, biomedical science students will focus more on the medical and healthcare side. On top of essential subjects like anatomy and clinical chemistry, you will also look into genetics, immunology, advanced pharmacology and other health related modules.
Having said that, since both fields are part of the bioscience field, you will share some similar subjects. This is primarily for introductory modules like microbiology and biochemistry.
Apply for university with EduAdvisor
Secure scholarships and more when you apply to any of our 100+ partner universities.
Start now#3. Biomedical science has a higher entry requirement compared to biotechnology
Can’t decide which field to pursue? Perhaps you can let your results guide you.
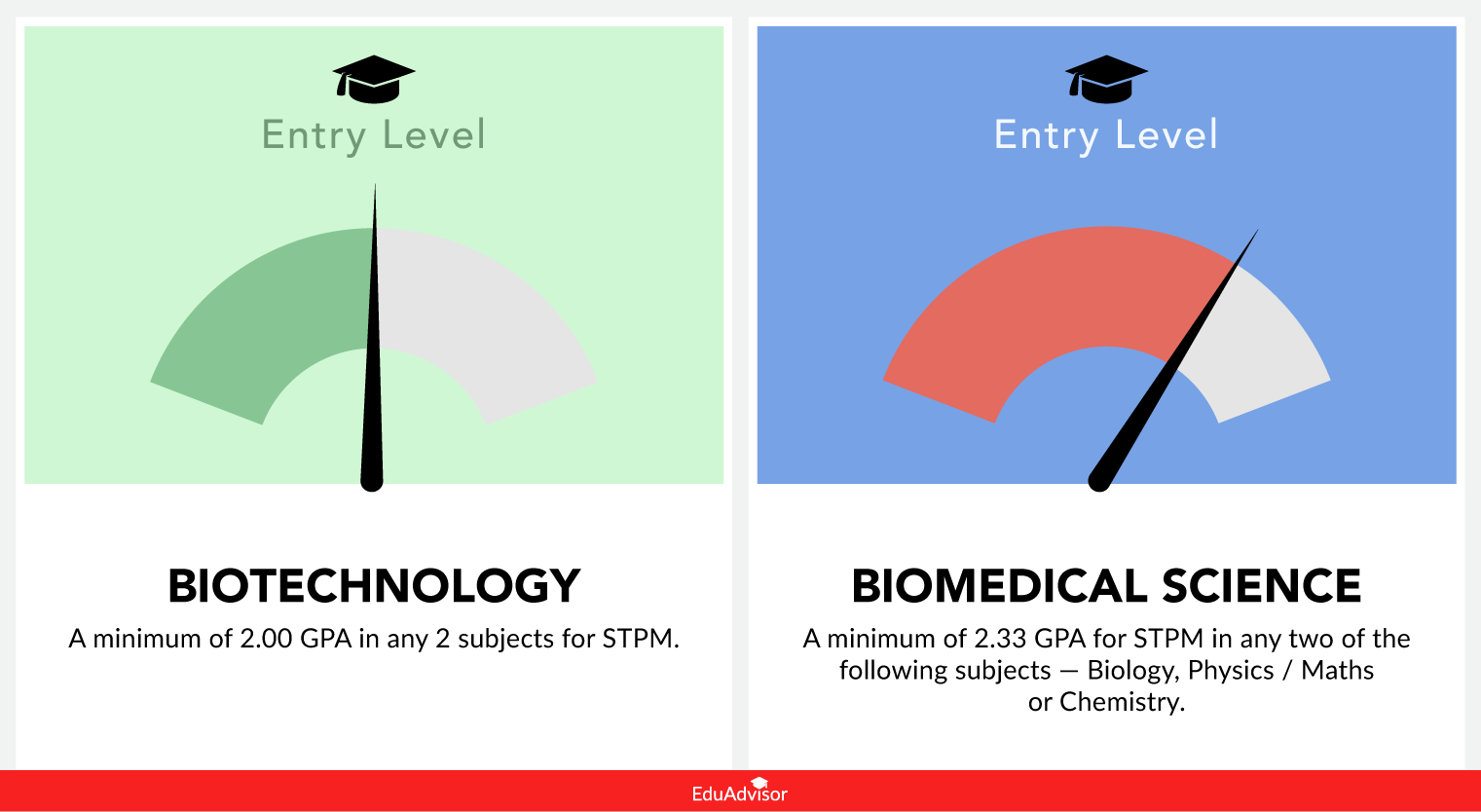
Between the two programmes, a biomedical science degree in Malaysia commands a higher entry requirement.
Specifically, to study biomedical science, MQA requires you to have at least a GPA of 2.33 at STPM (or equivalent) in two of the following subjects — Biology, Physics / Mathematics or Chemistry.
In contrast, biotechnology does not require you to have any background at STPM level. Instead, it calls for a GPA of 2.00 in any 2 subjects at STPM (or equivalent). However, you must have achieved 3 credits in SPM including Mathematics and one Science subject.

#4. Both fields have different career prospects
Biotechnology is a vast industry and you can find work in a myriad of fields. This includes environmental (research renewable technology, pollution control, etc.), industrial (work on safer and more resilient food products, develop enzymes for bio detergents, etc.) and marine biotechnology (increase yields of farmed fish, prevent aquatic life from succumbing to diseases, etc.).
For biomedical science graduates, your prospects revolve mainly around the healthcare and medical field, primarily in the research arena. You can be a biomedical scientist to help diagnose and treat diseases. You can also choose to focus on specific parts of medicine by becoming a clinical scientist in biochemistry, immunology or genomics.
It is crucial to note that you can still go into the healthcare industry even with a biotechnology degree. In fact, you can combine your skill sets with biomedical scientists to come up with life-saving drugs and procedures.
Similarly, your options are not limited to healthcare even if you graduate with a biomedical science degree. Your skill sets are needed in a variety of fields and you can seek out careers such as a medical sales representative, medical product specialist, science journalist and bioentrepreneur.
With so many various life forms to cover, it’s only natural for bioscience to branch out into various fields. Hopefully, this short guide has helped you gain a better understanding of the differences between biotechnology and biomedical science.