6 Unbelievable (and Scary) Things You Didn't Know Climate Change Can Do
Did you know that our ocean may be running out of fish? Here are 6 frightening effects of climate change that you didn’t know of!
Updated 26 Jan 2022

You’re probably familiar with the immediate effects of climate change such as heat waves, rising sea levels, wildlife species going extinct and melting glaciers. But what you may not know is that climate change can seriously impact the way we live. In fact, some might even seem downright impossible — but they’re extremely real.
Here are 6 scary and unusual impacts of climate change that we didn’t realise and why you should be concerned.
#1. Trigger more disease outbreaks
Mankind has gone through a series of pandemics such as SARS, H1N1 and now COVID-19. While we have managed to come up with vaccines and antidotes thanks to bioscience, it seems that we might need to brace ourselves for more disease outbreaks.
According to WHO, there will be a rapid increase of infectious disease as the temperature gets warmer. Environmental changes such as deforestation can lead to greater rainfall and new habitation. This directly links to booming populations of disease-carrying animals like mosquitoes and rats. These pests are responsible for the spread of malaria, dengue fever, lepstorspiroris, tularemia and Lyme disease.
In fact, the heat is also waking up bacteria and viruses that have been lying dormant in the permafrost. In 2016, a 12-year-old boy in Siberia died of anthrax believed to have come from a century-old reindeer carcass that thawed in a heat wave. This can explain new variants of zoonosis virus that are transmissible from animals to humans.
PRO TIP
Interested with what goes on behind the scenes in producing vaccines and antidotes to save the world? Start with a bioscience degree right here.
#2. Increase the frequency of sudden rainstorms
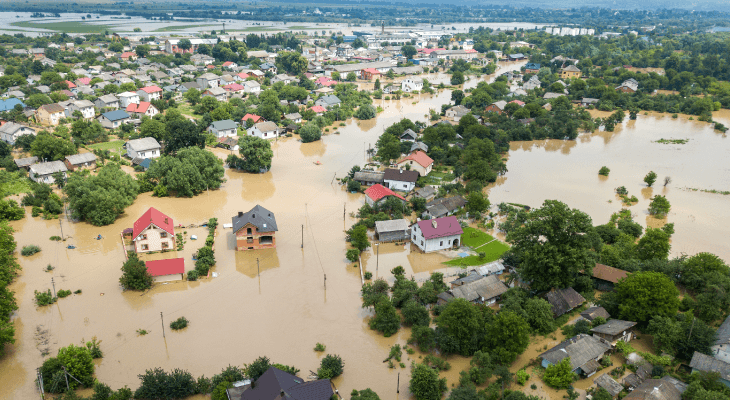

While Malaysia is known for its hot weather and the occasional rain, the recent weather we faced is quite unusual. Klang Valley was hit by one of the worst flash floods in years due to the 3 days of torrential rain, causing many areas to be submerged and damaging houses, roads and bridges.
Kuala Lumpur’s hot and humid weather can trigger deep convection, resulting in extreme weather such as flash floods, strong thunderstorms and hail. While this is a natural phenomenon, the intensity of the weather patterns is most likely due to climate change.
According to research, Kuala Lumpur has seen an increase of extreme rainfall by 35% over the past 3 decades due to urbanisation and climate change. And it’s only going to get worse when global temperatures increase. This means we’ll be seeing frequent and stronger storms and cyclones, so brace yourself!
#3. Impact plant breeding season
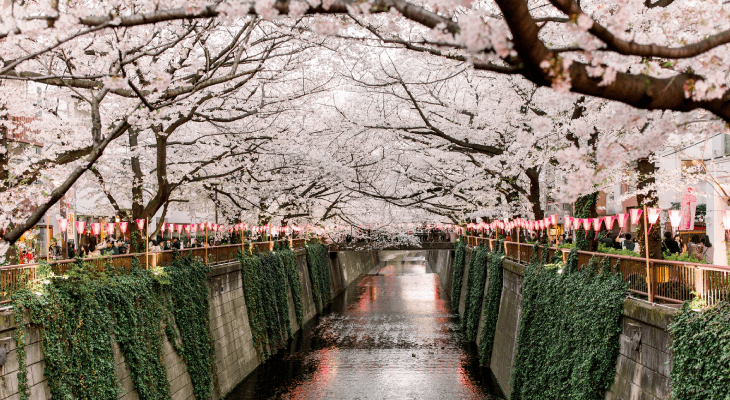

In Japan, the traditional sign of spring is the blossoming of sakura flowers which occurs between late March and early April. However, the cherry blossoms season in 2021 officially began on 14 March, the earliest bloom in 1,200 years ago.
This may not come across as news to many but the early blooming of cherry blossoms are concerning climate experts and here’s why you should be concerned too.
The early blooming is an indicator of warmer global temperatures. Changes in plant breeding seasons can have an adverse effect on the ecosystem because different species respond to different environmental cues. This means early pollination season, migration of birds and shortage of vital food supply. Ultimately, it can shift the entire food chain especially between species that are dependent on each other.
Despite the positive effects on agriculture from climate change such as the boost of rice, soybean and wheat from rising carbon dioxide, the negative effects such as unpredictable and extreme weather are causing shortages of common food due to heavy rainfall and floods.

#4. Shrink the size of animals

Did you know that chickens, elephants, crocodiles, sea turtles and even platypuses are living descendants of dinosaurs and prehistoric animals?
A recent study shows that Earth's two massive heating periods around 55 million years ago caused at least three species of mammals to shrink. But history is about to repeat itself as modern animals are starting to decrease in size due to climate change.
The reason for this shrinking comes down to basic survival. As nutrients become scarce, their smaller size helps them to reduce their energy needs, survive on lesser food and cool off easily in hot climates. While it may take longer to be apparent, we might see our modern animals such as polar bears, birds, spiders and oysters get smaller as temperatures increase in time.
If you’re concerned whether humans will shrink too, the answer is no. According to Professor Philip Gingerich of the University of Michigan, humans are unlikely to be affected by heating periods as we’re high on top of the food chain. Dwarfism due to climate change are more likely to affect herbivores and wild animals due to drought and limited food.
Apply for university with EduAdvisor
Secure scholarships and more when you apply to any of our 100+ partner universities.
Start now#5. Turn ocean waters darker

If you think that the triumphant blue colour of the ocean is a sight to behold, think again. Scientists are suggesting that a darker hue is a sign that the world’s ocean is growing more acidic due to climate change.
However, it’s not the colour of the water that changes. Instead, it’s the decrease of marine phytoplankton as seawater warms. These organisms contain green pigment chlorophyll to produce oxygen and nutrients for other organisms through photosynthesis. Any change in their numbers affects the water’s apparent colour.
This will not only affect marine organisms but humans as well. Phytoplankton serves as a food source for small sea creatures, which are in turn food sources for fish, squid and shellfish. If phytoplankton populations decrease, it will affect the entire food chain by limiting the source of protein for people.
While the colour shift will be too subtle to be seen by the naked eye, satellites will be able to spot the difference. This alerts the scientists that our marine ecosystems have undergone a potentially ominous shift.
#6. Cause bumpier flights

If you think bumpy flights are already stressful, you may need to buckle up (properly) because air turbulence is about to get worse due to climate change.
Air turbulence can be caused by many things — wind, storms or jet streams. Essentially,it occurs when an airplane flies through irregular or violent waves of air that causes the aircraft to bounce or roll. But as the earth starts to increase in temperature and warms the atmosphere, jet streams will move faster, thus making airplanes more susceptible to turbulence. In fact, based on a 2007 study, turbulence has increased by 40% since the 1950s!
If you’re one to already have aviophobia (fear of airplanes), we suggest you sit this one out.
There’s already observable effects on climate change but the fight doesn’t stop here. Stopping global warming may take years but with enough determination, passion and awareness, we can put in the effort to slow it down.




